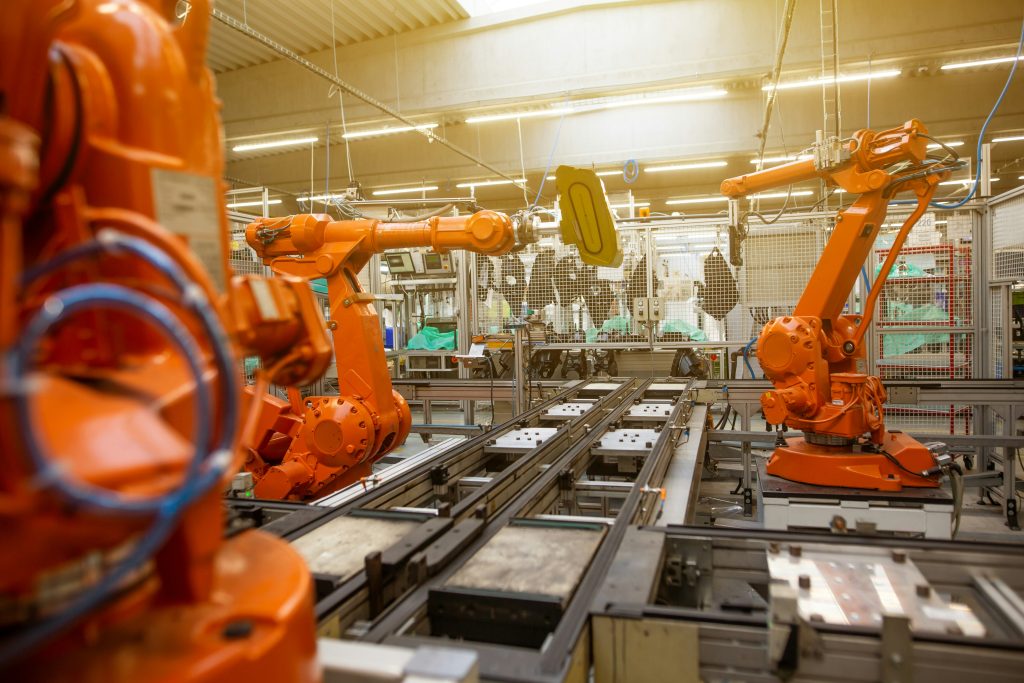
The automotive industry is at the forefront of the global push for sustainability, evolving rapidly to meet environmental challenges and societal demands for greener practices. Over the decades, car manufacturing has transformed from resource-intensive processes to innovative, eco-friendly approaches aimed at reducing carbon footprints and preserving natural resources. Here’s an exploration of how sustainable car manufacturing has evolved and the key areas driving this transformation.
Material Innovation: Reducing Environmental Impact
The materials used in car manufacturing have undergone significant changes, with manufacturers shifting toward recycled and sustainable alternatives.
Recycled Materials: Automakers are increasingly using recycled plastics, metals, and fabrics in vehicle production. For example, BMW’s i3 incorporates recycled carbon fiber and natural fibers in its construction.
Biodegradable Materials: Research into biodegradable materials, such as bio-based plastics and plant-derived composites, is advancing, reducing reliance on petroleum-based products.
Lightweight Designs: Lightweight materials, including aluminum and carbon fiber, are being used to improve fuel efficiency and reduce energy consumption during manufacturing.
Energy-Efficient Manufacturing Processes
Car manufacturing facilities have embraced energy-efficient practices to minimize their environmental impact.
Renewable Energy: Many automakers, including Tesla, Ford, and Toyota, have transitioned their factories to run on renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
Energy-Saving Technologies: Advanced robotics and AI are optimizing assembly lines, reducing energy consumption and minimizing waste.
Water Conservation: Manufacturers are implementing closed-loop water recycling systems, significantly reducing water usage in processes like paint application.
Circular Economy Practices
The concept of a circular economy is reshaping how automakers design, produce, and recycle vehicles.
End-of-Life Vehicle Recycling: Companies are creating systems to recover and reuse materials from old cars, reducing landfill waste and conserving resources.
Battery Recycling: With the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), recycling programs for lithium-ion batteries are becoming a priority. Recovered materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel are reused in new batteries.
Second-Life Batteries: Batteries from EVs are repurposed for energy storage in homes and commercial applications, extending their usefulness.
Cleaner Production Techniques
Manufacturers are adopting cleaner production techniques to reduce emissions and environmental harm.
Low-Emission Paint Shops: New paint application technologies are cutting emissions from volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Waste Minimization: Factories are reducing and repurposing production waste, such as metal scraps and excess plastic.
Carbon-Neutral Goals: Leading automakers, including Volvo and Mercedes-Benz, have committed to making their manufacturing operations carbon-neutral by the next decade.
Integration of Electric Vehicle (EV) Manufacturing
The rise of EVs has revolutionized car manufacturing, necessitating a complete rethink of traditional production methods.
Dedicated EV Plants: Automakers are building specialized factories focused exclusively on EV production, with lower emissions compared to traditional plants.
Battery Gigafactories: Large-scale battery production facilities, like Tesla’s Gigafactories, are setting benchmarks for sustainable energy use and efficiency.
Localized Supply Chains: To reduce emissions associated with transporting materials, manufacturers are focusing on localized production and sourcing.
Supply Chain Transparency and Responsibility
Sustainability in car manufacturing extends beyond factories to include the entire supply chain.
Ethical Sourcing: Automakers are working to ensure raw materials, such as lithium and cobalt, are sourced responsibly, avoiding environmental degradation and unethical labor practices.
Supplier Collaboration: Partnerships with suppliers are fostering innovation and enabling the adoption of greener practices throughout the supply chain.
Digital Tracking: Blockchain technology is being used to track materials and components, ensuring accountability and transparency in sourcing.
Consumer Influence and Regulatory Pressure
Consumer demand and government regulations have accelerated the adoption of sustainable practices.
Eco-Conscious Buyers: Consumers are increasingly choosing brands that demonstrate environmental responsibility, pushing automakers to adopt greener practices.
Regulatory Compliance: Stringent emissions and sustainability regulations in regions like Europe and California are driving innovation in sustainable manufacturing.
Incentives for Green Vehicles: Government subsidies and incentives for EVs encourage manufacturers to shift their focus to sustainable production.
Driving Toward a Greener Future
The evolution of sustainable car manufacturing is far from complete. As the automotive industry faces growing pressure to reduce its environmental impact, advancements in technology, collaboration across supply chains, and shifts in consumer behavior will continue to drive innovation.
Automakers are now balancing sustainability with profitability, investing in research and development to create vehicles that are not only efficient on the road but also eco-friendly from conception to disposal. This transformation reflects a broader commitment to sustainability that promises a cleaner, greener future for transportation and beyond.